Are you struggling with poor wireless signal and range? It’s not just you. Despite the growing variety of wireless routers, There are many challenges that could limit the strength and range of the wireless connection. You can implement easy solutions, and many are entirely free. Before you give up and shell out more than you need on an expert, Here are ten easy ways to boost wifi signal strength.
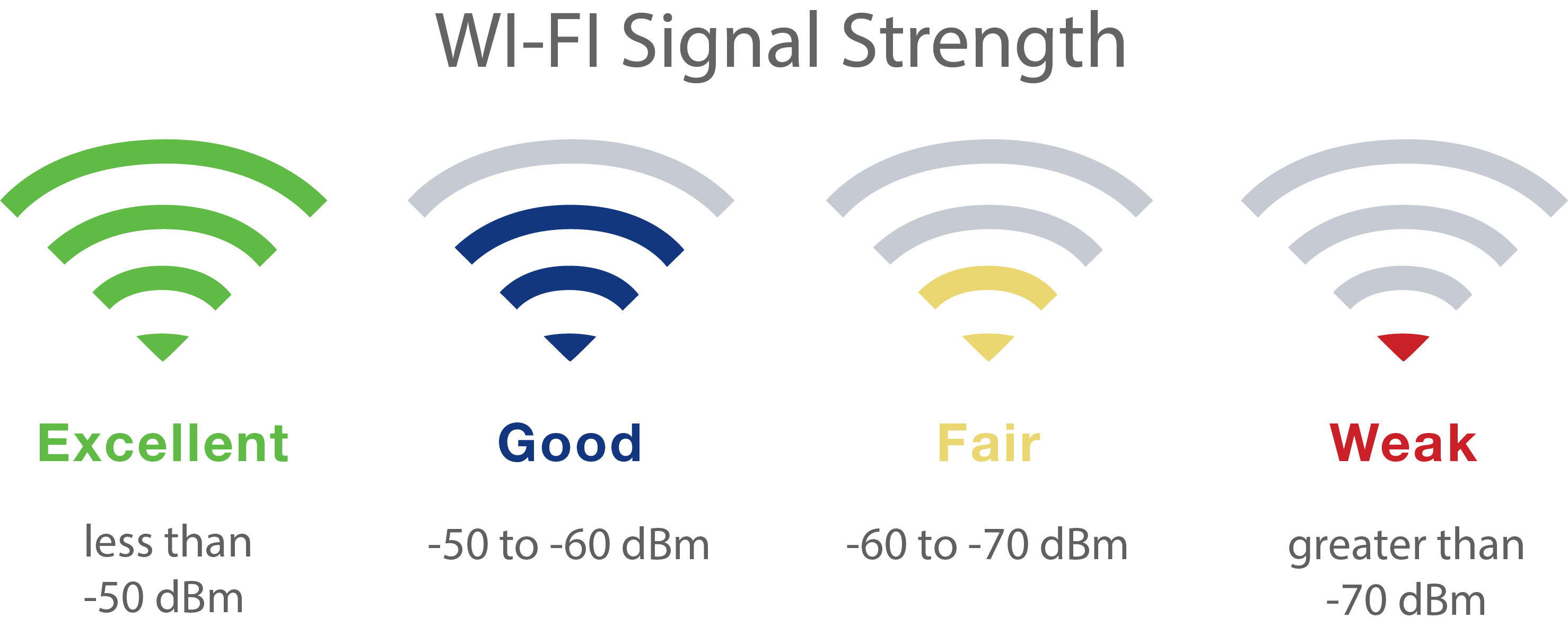
What is the reason I am experiencing weak wifi signal strength and softness?
Despite widespread use in our homes and lives, wireless internet technology is relatively new. While the first functioning “wireless internet” was presented during a show in Hawaii around 1970, years prior to the wireless technology was affordable and powerful enough to be practical at home.
As amazing as wireless networks are, they come with major limitations because of how they operate. Wireless networks and signals use radio frequency transmissions, similar to your car, your home radio, or even over-the-air television. The signals utilized by wireless networks are at frequencies different from those your microwave produces naturally, as well as those radio stations broadcast to your car.
Since the wireless network transmits via radio frequencies, the network may be affected by the same limitations that are typically encountered in other radio signals. Therefore, your wireless network at home may be insufficiently strong or coverage due to the same limitations that affect other types of radio technology.
- Obstacles that result in a decrease in signal strength
- Interference by other devices emitting radio waves
- Less reliable signals are sent out by less effective and older wireless equipment
- Issues with the technical aspects of the receiver device can cause the movement to appear weak
- Insufficient power from the wireless router, resulting in weaker signals
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) determines the standards for wireless radio networks that are permitted to utilize. The wireless networking equipment at home could operate in the band of 900MHz or the 2.4, 3.6, 5, or even the 60 GHz frequency band. The majority of routers in homes use bands of 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz bands.
Before you attempt to resolve your problems that involve weak or range, look up the frequencies your router or networking equipment is using. This knowledge can assist you in solving the issues with strength and range.
How can you improve the wifi signal and strength?
Ultimately, it can be complicated to identify the root of your weak wireless network or range. It is recommended to try the steps listed in sequence before buying a new router. If you find that none of the DIY alternatives work, then purchasing the new router might solve your network issues.
1 Switch your router into a central area
Here’s a “rule to follow” to follow that your typical wireless router can reach a distance between 150 feet (46 meters) indoors and 300 feet (92 meters) outdoors. While this should be enough for a typical house or apartment, various obstructions and signal interferences could make the signal weaker before it can reach different areas in your residence.
The location you put the router will affect how well you’re receiving the best possible coverage of signals. It all depends on the kind of router you’re using as well as its signal strength. No matter what, if your wireless router is tucked inside your office corner located in your basement or at the top of the level, you could have more problems with signal strength and range than you’re supposed to.
Consider the possibility of placing your router’s wireless connection in a central location. Many families put their routers close to computer equipment in their home offices. But, you can put your router anywhere within your home. With an average distance of a wireless router being 150 yards, an ideally placed router can better connect to the entirety of an average-sized home.
2 Identify any equipment that may be causing interference
Wireless networks use radio frequency signals to transmit and receive information; there’s a possibility that your wireless signal might be weak because of interference from devices that transmit radio signals. These devices could block wireless transmissions:
- Microwave
- A few electric power Sources (such as power lines)
- Wireless audio equipment
- External monitors
- Baby monitors
- Wireless cameras
- RF video transmitters
- Telephones that are cordless
- Certain satellite TV receivers
In general, the use of wireless technology of different kinds is only growing. This means you could use a variety of wireless equipment that transmit messages throughout the home. If any of the equipment operates the same way as the wireless router, then interference will occur.
You’ll be able to tell if you’re dealing with a signal interference issue when any of the following statements are the case:
- Wireless devices constantly show weak signal strength or signal strength appears to fluctuate even when you’re not switching your location.
- You will experience a slower Internet connection when you connect to wifi.
- Your rate of file transfer is affected when you connect to wifi.
- Bluetooth devices have trouble pairing
- It is common for internet connections to be lost.
If you suspect there could be interference issues, switch off all other devices that are transmitting wireless signals in order. Examine whether there’s a change in signal strength or the range after turning off all devices. If you notice a significant difference after each device is switched off, you’ve discovered one of the causes.
In a situation that is not yours, The best solution would be to relocate your router from the device that is possible, or better yet, move the device that is interfering. Limiting the number of wireless devices you can have within your home at a given time is generally recommended.
3 Change your wireless router channel

This suggestion is entirely dependent on the wireless router you have. If you’re in an apartment or an urban area with a lot of people, problems with wireless interference might be caused by the wifi router of your neighbor.
It is sometimes difficult to tell if this is a problem. However, if you are using the internet on any device, for example, the mobile phone or computer, You can determine the number of wireless signals within the range. The more devices you can connect to, the greater chance that your neighbor’s wifi device may be causing problems for yours.
Switching your wireless router’s channel will enable it to work in a slightly different portion of the frequency spectrum, eliminating the issue of interference. How to change the channel can differ based on your device and model. Go through the manual for your device or visit the manufacturer’s website for information on how to change your channel’s settings.
4 Limit your number of gadgets taking the bandwidth
Problems with signal strength and the low signal could cause problems with devices and applications connected to your internet. Things that could be substantial bandwidth drainers include:
- Gaming online
- Netflix
- Spotify
- Calling video
- Torrenting
- streamable HD videos
- Sharing of files
- Utilizing cloud-based applications
- Malware
If devices are using the majority of your bandwidth, they could result in slow-downs on other devices, giving the appearance of weak signal strength.
Try to reduce the number of devices you use to consume the bandwidth of your internet at the moment. If you plan to stream video in high-quality and play on the internet, you should try making it happen without having multiple devices operating at the same time.
You can automate the process in the event that your router is using QoS or Quality of Service (QoS) methods. These techniques automatically prioritize operations in order to minimize problems with connectivity and bandwidth. Consult the router manual or the manufacturer of your device to determine whether your device is using Quality of Service and in the event that it does, how you can alter the settings on your device in order to use it.
5 Build an at-home wifi extender

Although it isn’t a sure-fire method you can make a tiny amount of range from your wifi router using DIY methods that make use of things like aluminum beer, foil, or automobiles, we also offer a thorough description of how to build your own wifi extender.
6 Install DDWRT in your router (if you’re able)
Wireless routers are all equipped with firmware (a type of software created to allow your hardware to function effectively) already installed. However, certain wireless routers can run third-party firmware to improve their capabilities. The most popular of these is known as DD-WRT.

The advantages of DD-WRT
The DD-WRT router can increase the speed of your wireless signal by allowing you to modify the settings of your router and adjust your frequency channel.
In addition, you can use the DD-WRT program to unlock the features on your router, which allows you to consume more electricity, which is an important factor in increasing the range of wireless signals. (Note that adjusting the amount of power your router draws could cause your device to overheat. Examine the amount of the device’s power that can draw in a safe manner prior to using the method).
7 Reset your router regularly
If you notice that your wireless signal strength and signal appear to decrease frequently or decrease, resetting your router can aid in improving the quality of your wireless signal. If you’ve previously observed the reset of your router can help with connectivity issues, you could utilize DD-WRT for a router reset to a consistent timetable each day.
8 Make an investment in the signal booster
Sometimes, all you require is an amplifier. Signal boosters are available in a variety of designs and sizes; however, they are made to boost the power of the signal to another device. They are sometimes referred to as “wifi repeaters” These devices are used to increase the strength and range of weak signals.
Netgear offers additional information about repeaters and boosters.
9 Make an investment in the latest router
The bottom line is that a handful of techniques are more effective at increasing the signal strength and range of wireless networks than investing in better equipment. If your router’s wireless signal isn’t expensive or up-to-the-date, there’s a high possibility that a lot of these techniques won’t work or only be able to work only to a limited extent.
Problems with old routers
Older routers usually have less efficient technology and could even experience technical issues, for example, issues with overheating, which can cause poor signal strength. In addition, the cheaper routers aren’t equipped with the right technology to perform efficiently over the long haul and, in general, lack the power output needed for greater coverage.
Consider this as it’s a “last-ditch” attempt. But, upgrading an older wireless router can become necessary because wireless standards are changing and technology improves to support more receivers.
10 Adjust your router antenna
If this is you, then you don’t have a powerful wifi router with antennae. But, if your router is one of the routers with several antennas, changing the direction of these antennas can improve the signal.
It’s easy to believe that pointing your wifi antenna straight ahead is the correct way to go about things. However, this isn’t the case in virtually every situation.
In the event that you’re using a 2.4 GHz router, make sure you point the antennas perpendicularly. g. an antenna that is pointed vertically and one-pointed horizontally, creating an L-shaped shape. If you are using 5 GHz, make sure to point them straight out or at a 45-degree angle to achieve the most effective results.
The former Apple wifi engineer has shared some tips in Mac Observer. Check out the details and more tips from him on this page. In addition, you can access some interesting information in DSLReports from a professional in networking who conducted a test with both frequencies.
Bonus Tip: Wifi bands have a positive impact
It was mentioned previously that there are a variety of wifi frequency bands your router may use that are available, with 2.4 5GHz and 2.4 GHz being the most commonly used. The frequencies you are using can affect the strength of your wifi signal as well as coverage.
It is important to keep in mind that wifi signals can be described as radio signals. Higher frequencies travel more quickly, but they travel farther, and lower frequencies travel further but are slower.
If you’ve got a huge home and are using five GHz bands, you have a high chance that shifting your router will solve your issue.
If you’re using a 2.4 center frequency router, the slow speed could be due to the lesser bandwidth offered by 2.4 5GHz routers. It is possible to upgrade to 5 GHz, which is a better option for streaming media and heavy bandwidth use.